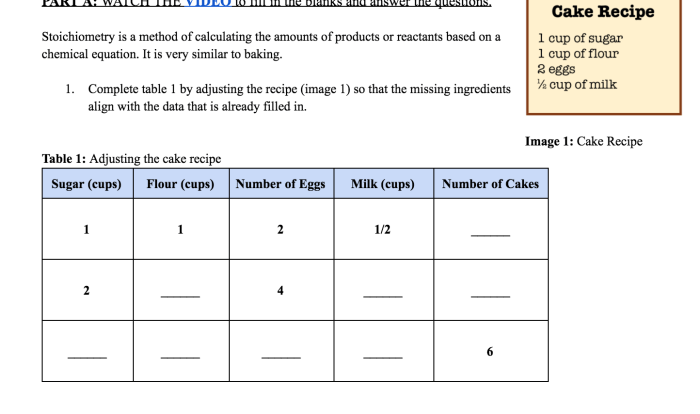
A solution contains 35 grams of kno3 – A solution containing 35 grams of potassium nitrate (KNO3) presents a fascinating case study in chemistry. This compound, with its unique properties and diverse applications, offers a rich tapestry of knowledge to explore. Join us as we delve into the composition, concentration, and practical uses of this intriguing substance.
Potassium nitrate, a salt composed of potassium, nitrogen, and oxygen, possesses a crystalline structure and is highly soluble in water. Its chemical formula, KNO3, reflects its ionic composition, with potassium ions (K+) and nitrate ions (NO3-) forming a stable lattice.
This compound exhibits a range of physical and chemical properties that contribute to its versatility in various fields.
Composition and Properties of Potassium Nitrate (KNO3)
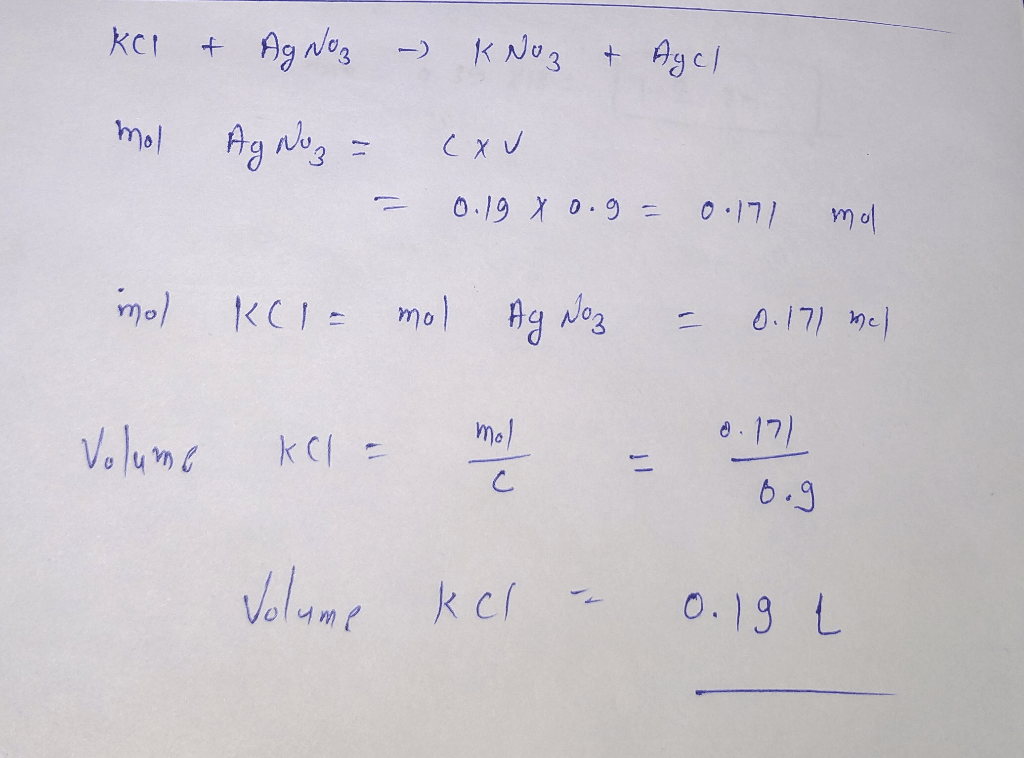
Potassium nitrate (KNO3), also known as saltpeter, is a chemical compound composed of potassium, nitrogen, and oxygen. It is a white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water.
Potassium nitrate has several important physical and chemical properties. It is a strong oxidizing agent and can be used to make explosives. It is also a fertilizer and can be used to preserve food.
Solubility and Reactivity
Potassium nitrate is highly soluble in water. The solubility of KNO3 in water increases with temperature. At 25 °C, the solubility of KNO3 is 31.6 g/100 mL of water.Potassium nitrate is a reactive compound. It can react with a variety of other chemicals, including metals, acids, and bases.
Concentration of Potassium Nitrate Solution: A Solution Contains 35 Grams Of Kno3
The concentration of a solution is a measure of the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent. The concentration of a potassium nitrate solution can be expressed in terms of molarity.
Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. The molarity of a potassium nitrate solution can be calculated using the following formula:
“`Molarity = moles of KNO3 / liters of solution“`
Converting Grams per Liter to Molarity
The concentration of a potassium nitrate solution can also be expressed in terms of grams per liter (g/L). The concentration in g/L can be converted to molarity using the following formula:“`Molarity = (grams of KNO3 / liter of solution) / molar mass of KNO3“`The molar mass of KNO3 is 101.1 g/mol.
Mass-to-Volume Calculations

The mass of potassium nitrate present in a solution can be determined using the following formula:“`Mass of KNO3 = Molarity of solution × Volume of solution × Molar mass of KNO3“`
Example
A solution contains 35 grams of KNO3. The volume of the solution is 1 liter. What is the mass of potassium nitrate present in the solution?“`Mass of KNO3 = (35 g / 1 L) × 101.1 g/mol = 3538.5 g“`
Dilution and Concentration
Dilution is the process of adding more solvent to a solution. When a solution is diluted, the concentration of the solution decreases.
The new concentration of a solution after dilution can be calculated using the following formula:
“`New concentration = (Original concentration × Original volume) / (Original volume + Volume of solvent added)“`
Example
A solution contains 1 M KNO3. The volume of the solution is 1 liter. What is the concentration of the solution after 500 mL of water is added?“`New concentration = (1 M × 1 L) / (1 L + 0.5 L) = 0.67 M“`
Applications of Potassium Nitrate

Potassium nitrate has a variety of applications, including:
- Fertilizers
- Explosives
- Food preservation
Fertilizers
Potassium nitrate is a common ingredient in fertilizers. It is a source of nitrogen and potassium, which are essential nutrients for plants.
Explosives, A solution contains 35 grams of kno3
Potassium nitrate is a strong oxidizing agent and can be used to make explosives. It is a component of black powder, which is used in fireworks and firearms.
Food preservation
Potassium nitrate is used as a food preservative. It is added to meat and fish to prevent the growth of bacteria.
Safety Considerations
Potassium nitrate is a hazardous substance and should be handled with care. It is important to wear gloves and eye protection when working with potassium nitrate.
Potassium nitrate should be stored in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials. It should also be kept out of the reach of children.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the molarity of a solution containing 35 grams of potassium nitrate in 1 liter of water?
To calculate the molarity, we divide the number of moles of potassium nitrate by the volume of the solution in liters. The molar mass of KNO3 is 101.1 g/mol. Therefore, the number of moles in 35 grams is 35 g / 101.1 g/mol = 0.346 moles.
Thus, the molarity of the solution is 0.346 moles per liter (M).
How can we dilute a solution containing 35 grams of potassium nitrate to a concentration of 0.1 M?
To dilute the solution, we need to add more water to it. The formula for dilution is C1V1 = C2V2, where C1 is the initial concentration, V1 is the initial volume, C2 is the final concentration, and V2 is the final volume.
We know that C1 = 0.346 M, V1 = 1 L, and C2 = 0.1 M. Solving for V2, we get V2 = C1V1 / C2 = 0.346 M – 1 L / 0.1 M = 3.46 L. Therefore, we need to add 2.46 L of water to the original solution to achieve a concentration of 0.1 M.