Embark on a mathematical adventure with our “Integers and Their Opposites Worksheet”! This comprehensive guide unlocks the mysteries of number theory, providing a clear and engaging exploration of integers and their fascinating properties.
Delve into the world of positive and negative numbers, discover the rules for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing integers, and uncover their real-world applications. Prepare to expand your numerical horizons as we unravel the complexities of this fundamental concept.
Integers and their Opposites
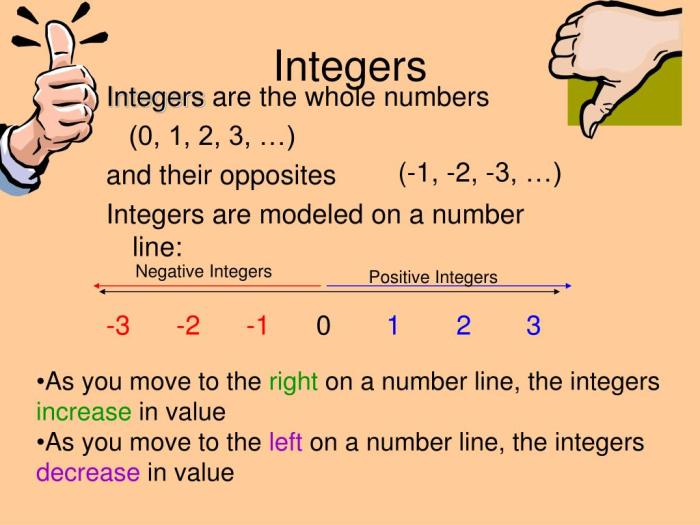
Integers are whole numbers that can be positive, negative, or zero. They are used to represent quantities that can be counted, such as the number of apples in a basket or the temperature in degrees Celsius.
Positive integers are greater than zero, and negative integers are less than zero. Zero is neither positive nor negative.
Examples of Integers
- 5
- -3
- 0
- 12
- -10
Adding and Subtracting Integers
To add integers, simply add their absolute values (the numbers without the signs) and keep the sign of the integer with the greater absolute value. If the integers have the same sign, add their absolute values and keep that sign.
To subtract integers, subtract the absolute value of the subtrahend (the number being subtracted) from the absolute value of the minuend (the number being subtracted from) and keep the sign of the minuend. If the minuend is negative and the subtrahend is positive, add their absolute values and keep the negative sign.
Rules for Adding and Subtracting Integers
| Operation | Rule |
|---|---|
| Adding integers with the same sign | Add the absolute values and keep the sign. |
| Adding integers with different signs | Subtract the absolute values and keep the sign of the integer with the greater absolute value. |
| Subtracting integers with the same sign | Subtract the absolute values and keep the sign of the minuend. |
| Subtracting integers with different signs | Add the absolute values and keep the sign of the minuend. |
Examples of Adding and Subtracting Integers
- 5 + 3 = 8
- -3 + 5 = 2
- 5 – (-3) = 8
- -3 – 5 = -8
Multiplying and Dividing Integers
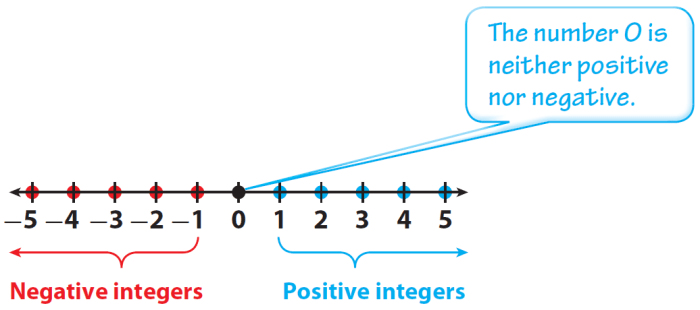
To multiply integers, simply multiply their absolute values and keep the sign of the product as follows:
- Positive x Positive = Positive
- Positive x Negative = Negative
- Negative x Positive = Negative
- Negative x Negative = Positive
To divide integers, divide the absolute value of the dividend (the number being divided) by the absolute value of the divisor (the number dividing into the dividend) and keep the sign of the quotient as follows:
- Positive ÷ Positive = Positive
- Positive ÷ Negative = Negative
- Negative ÷ Positive = Negative
- Negative ÷ Negative = Positive
Rules for Multiplying and Dividing Integers, Integers and their opposites worksheet
| Operation | Rule |
|---|---|
| Multiplying integers with the same sign | Multiply the absolute values and keep the positive sign. |
| Multiplying integers with different signs | Multiply the absolute values and keep the negative sign. |
| Dividing integers with the same sign | Divide the absolute values and keep the positive sign. |
| Dividing integers with different signs | Divide the absolute values and keep the negative sign. |
Examples of Multiplying and Dividing Integers
- 5 x 3 = 15
- -3 x 5 = -15
- 5 ÷ (-3) = -5/3
- -3 ÷ 5 = -3/5
Real-World Applications of Integers: Integers And Their Opposites Worksheet
Integers are used in a variety of real-world situations, including:
- Measuring temperature in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit
- Counting the number of steps taken or floors climbed
- Calculating profits and losses in business
- Representing the elevation of a mountain or the depth of a lake
- Determining the speed and direction of a moving object
Answers to Common Questions
What are integers?
Integers are whole numbers that can be positive, negative, or zero.
How do you add integers?
To add integers with the same sign, add their absolute values and keep the sign. To add integers with different signs, subtract the smaller absolute value from the larger and keep the sign of the integer with the larger absolute value.
What is the opposite of an integer?
The opposite of an integer is the integer with the same absolute value but the opposite sign.