Chapter review diffusion and osmosis – Chapter Review: Diffusion and Osmosis embarks on an authoritative exploration of the fundamental principles governing the movement of molecules and fluids across biological membranes. This comprehensive analysis delves into the mechanisms, significance, and applications of diffusion and osmosis, providing a thorough understanding of these essential biological processes.
Beginning with the concept of diffusion, the chapter elucidates its importance in biological systems and showcases its diverse applications in various biological contexts. Factors influencing the rate of diffusion are meticulously examined, laying the groundwork for a deeper comprehension of this ubiquitous phenomenon.
Diffusion: Chapter Review Diffusion And Osmosis

Diffusion is a fundamental process in biological systems, facilitating the movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. It plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, such as gas exchange, nutrient uptake, and waste removal.
Examples of diffusion in biological contexts include:
- Oxygen diffusing from the lungs into the bloodstream
- Carbon dioxide diffusing from the bloodstream into the lungs
- Nutrients diffusing from the small intestine into the bloodstream
- Waste products diffusing from cells into the bloodstream
The rate of diffusion is influenced by several factors, including:
- Concentration gradient: The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to faster diffusion
- Surface area: Larger surface areas facilitate faster diffusion
- Distance: Shorter distances between molecules promote faster diffusion
- Molecular size: Smaller molecules diffuse faster than larger molecules
Osmosis
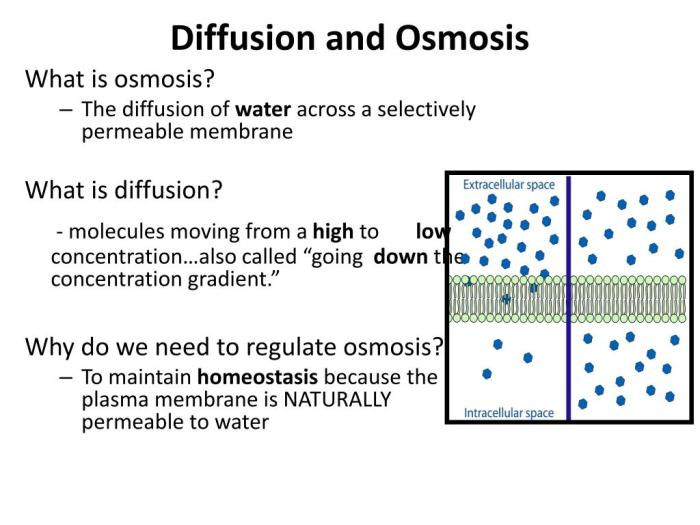
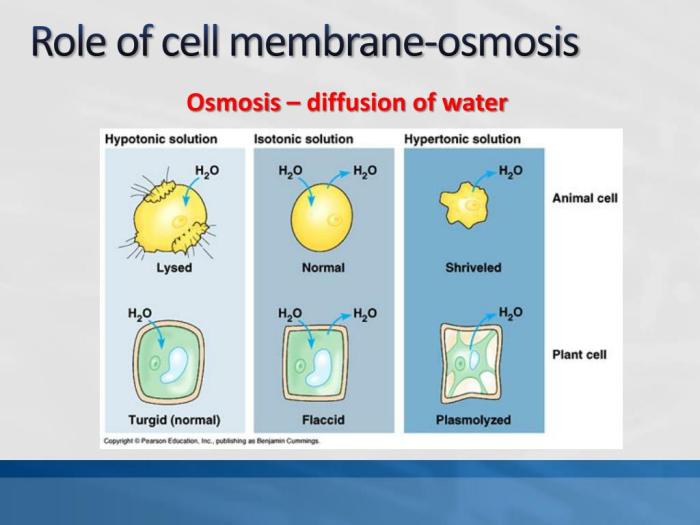
Osmosis is the net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. It is a fundamental process in biological systems, as it allows cells to maintain their proper water balance and function.
Significance of Osmosis in Biological Systems
- Cell volume regulation:Osmosis helps cells maintain their optimal size and shape by controlling the flow of water across their membranes.
- Nutrient and waste transport:Osmosis facilitates the movement of nutrients into cells and waste products out of cells.
- Plant growth and development:Osmosis is essential for the uptake of water by plant roots and the transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Osmosis
The rate of osmosis is influenced by several factors:
- Concentration gradient:The greater the difference in water concentration between the two sides of the membrane, the faster the rate of osmosis.
- Membrane permeability:The permeability of the membrane to water molecules affects the rate of osmosis. More permeable membranes allow for faster osmosis.
- Surface area of the membrane:A larger surface area of the membrane allows for more water molecules to pass through, increasing the rate of osmosis.
- Temperature:Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of water molecules, leading to a faster rate of osmosis.
Comparison of Diffusion and Osmosis
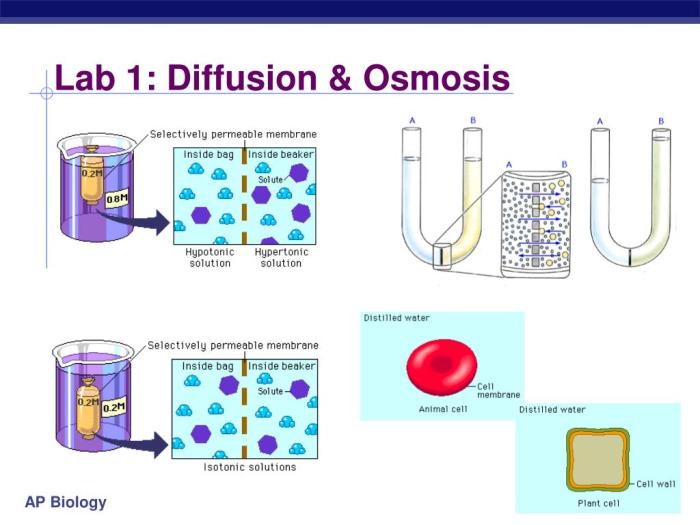
Diffusion and osmosis are two essential processes that facilitate the movement of molecules across semipermeable membranes in biological systems. While both processes involve the net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, they differ in their specific mechanisms and applications.
Mechanisms of Diffusion and Osmosis
Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration, driven by the random motion of molecules. In contrast, osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
The semipermeable membrane allows water molecules to pass through but restricts the passage of other molecules, such as ions and larger molecules.
Applications in Biological Systems
Diffusion plays a crucial role in transporting nutrients, gases, and waste products across cell membranes. It is essential for cellular respiration, nutrient uptake, and waste removal. Osmosis, on the other hand, is particularly important in regulating water balance in cells and tissues.
It helps maintain cell turgor, prevents cell shrinkage, and ensures proper cellular function.
Table: Key Differences between Diffusion and Osmosis
| Feature | Diffusion | Osmosis ||—|—|—|| Mechanism | Movement of all molecules from high to low concentration | Movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane || Driving force | Random motion of molecules | Water concentration gradient || Selectivity | Non-selective | Selective for water molecules || Role in biological systems | Transport of nutrients, gases, and waste | Regulation of water balance |
Applications of Diffusion and Osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis play crucial roles in numerous fields, including medicine, biotechnology, and environmental science. These processes have enabled significant advancements in healthcare, industrial processes, and environmental monitoring.
In medicine, diffusion and osmosis are essential for drug delivery, nutrient absorption, and waste removal. Osmotic pressure is utilized in dialysis to remove toxins from the blood, while diffusion principles guide the development of targeted drug delivery systems.
Biotechnology, Chapter review diffusion and osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis are fundamental to biotechnology applications. In genetic engineering, they facilitate the transfer of genetic material across cell membranes. Osmosis is also employed in the production of biofuels, where it helps separate ethanol from fermentation broth.
Environmental Science
In environmental science, diffusion and osmosis are used to monitor pollution levels. Diffusion rates can indicate the spread of pollutants in air and water, while osmosis is employed in desalination processes to provide clean drinking water in regions with limited freshwater resources.
However, it’s important to acknowledge potential limitations and challenges associated with these applications. For instance, in drug delivery, diffusion barriers can limit drug penetration into target tissues. In biotechnology, osmotic stress can affect cell viability and productivity. In environmental science, diffusion and osmosis can be influenced by factors like temperature and pH, which may require careful consideration and optimization.
FAQ Explained
What is the key difference between diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion involves the movement of molecules down a concentration gradient, while osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane.
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
Temperature has a positive correlation with the rate of diffusion; higher temperatures accelerate the movement of molecules.
What are some practical applications of osmosis?
Osmosis finds applications in various fields, including desalination, reverse osmosis water purification, and medical procedures like dialysis.